| HOME |
|---|
COLUMBA
The Dove
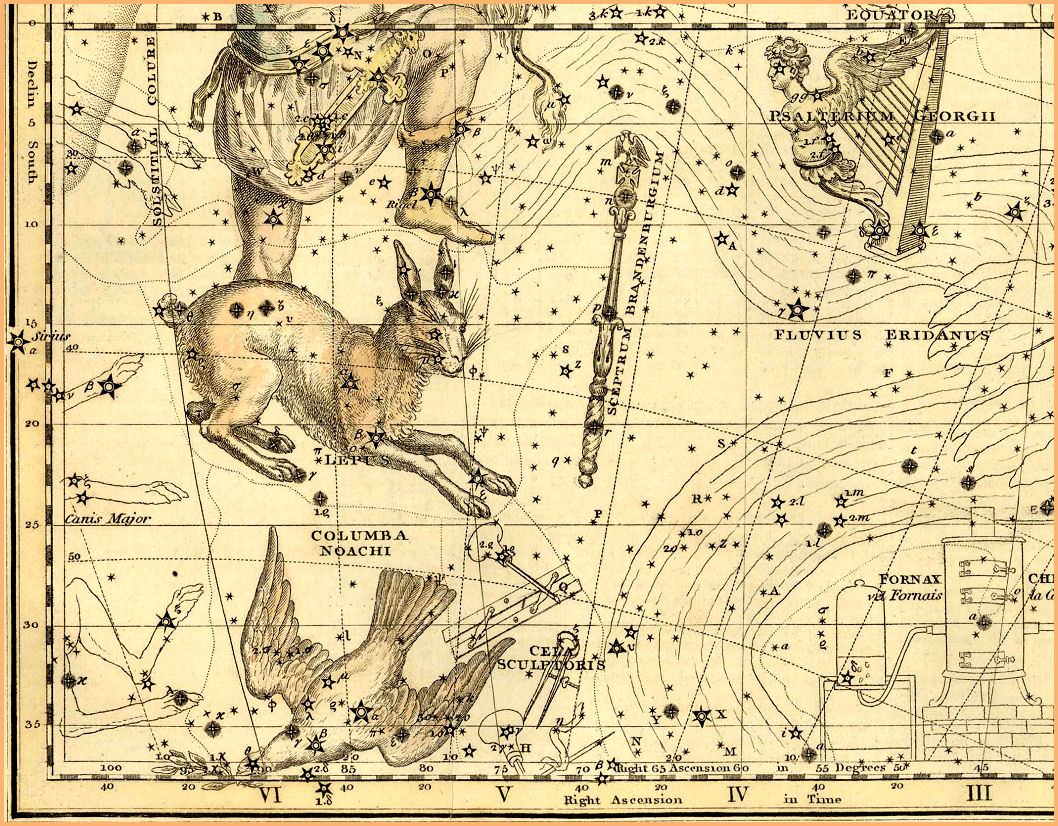
Columba - Celestial Atlas by Alexander Jamieson - 1822
| HOME |
|---|

Columba is a small, faint constellation first introduced by Dutch astronomer Petrus Plancius in 1592. Originally named "Columba Noachi", meaning Noah's Dove, it was meant to represent the dove that left Noah's Ark to look for dry land, and returned with an olive branch in its beak to signify the end of the flood.
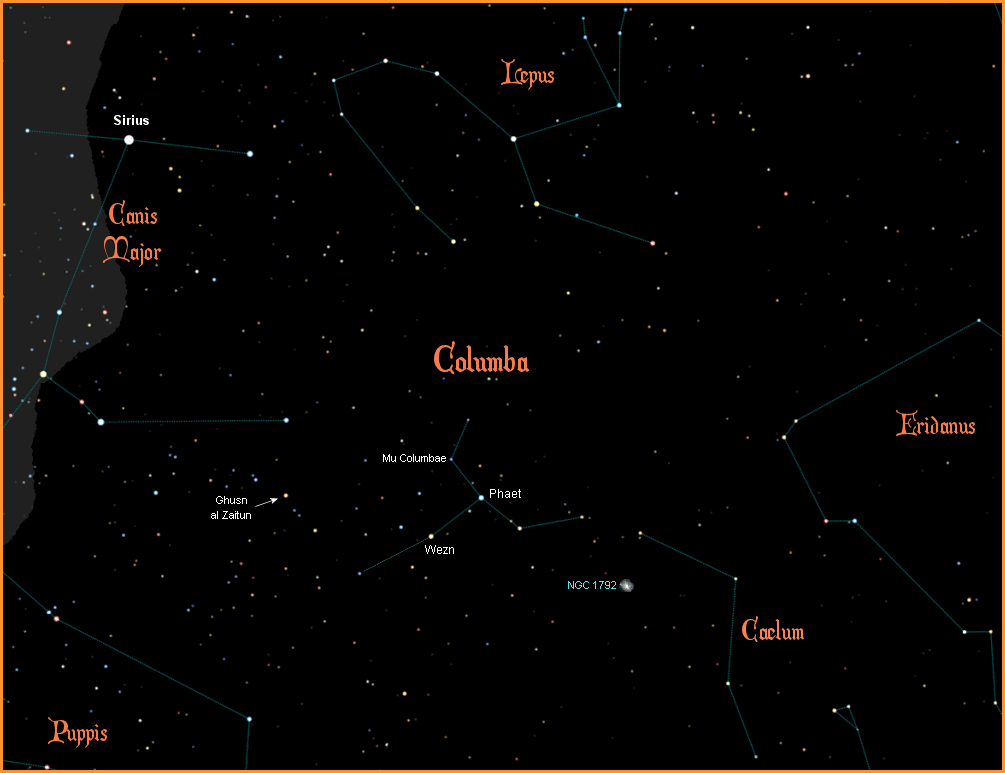
Alpha Columbae is named Phaet, from the Arabic "Al Fakhita", the dove. It is a B9V blue/white main sequence star, about 260 light years away. With amagnitude of 2.65, it is the brightest star in the constellation.
Beta Columbae is named Wezn, from the Arabic for weight. It is a K1III orange giant, located at a distance of 82 light years. With a magnitude of 3.1, it is the second brightest star in the constellation.
Delta Columbae is named Ghusm al Zaitun, the olive branch. It marks the end of the olive branch the dove brought back to Noah, showing the emergence of dry land after the flood. It is a G7II yellow bright giant, about 237 light years away. At magnitude 3.85, it is the third brightest star in the constellation.
Mu Columbae does not have a name, but is a well known runaway star that is moving at a much higher speed and in a different direction than the surrounding stars. It is moving in direct opposition to the star AE Aurigae in the constellation Auriga at a speed of 200 kilometers per second. The origins of both these stars can be traced back to the Great Orion Nebula, where interactions between binary systems or perhaps a supernova explosion caused the stars to be ejected from the nebula. Mu Columbae is an O9V blue main sequence star with a surface temperature of a sizzling 33,000 degrees C, making it 21,000 times brighter than our Sun. At a distance of 1,300 light years, it has a magnitude of 5.13.
So far only one star in Columba has been found to host a planet, but the star is extremely far away and dim, and the planet is a gas giant about a third the size of Jupiter. For more information on these and other extrasolar planets, visit NASA's New Worlds Atlas, and The Open Exoplanets Catalogue.
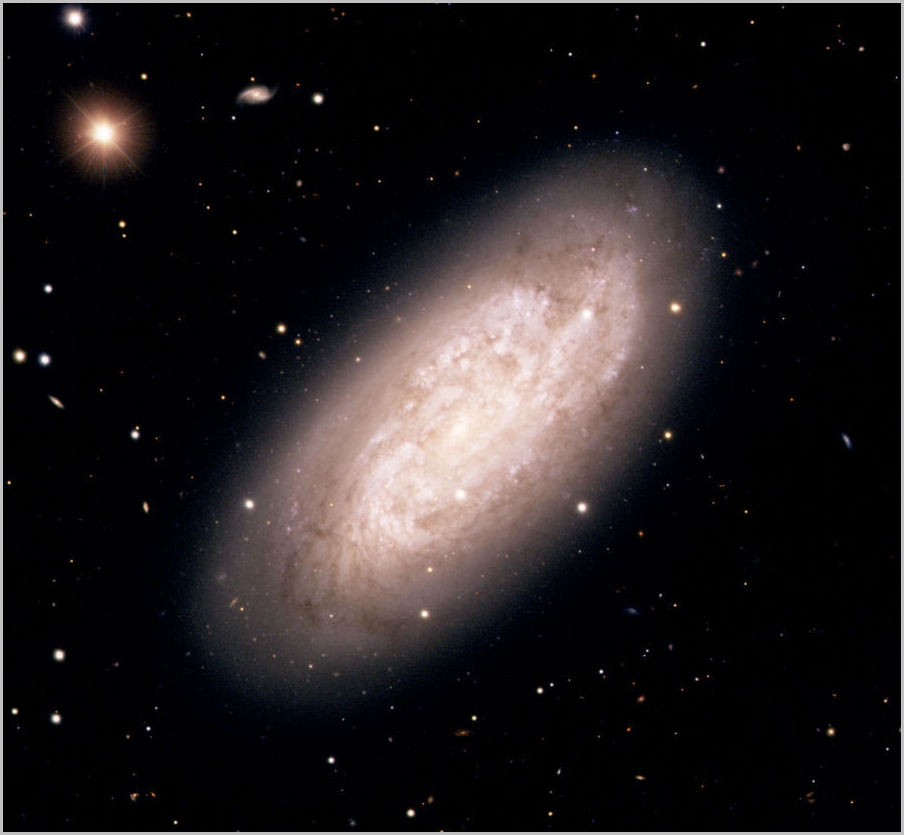
Columba contains the bright spiral galaxy NGC 1792, with a magnitude of 10.7. At a distance of 50 million light years, it is known as the Starburst Galaxy because of the rapid rate of new star formation within it.

|
|
|
|
|
|